Applies to Platform: UTM 2.4, UTM 2.5; 4i Edge 2.5
Last Updated: 27 May 2014
Applies to Platform: UTM 3.0, 4i Edge 3.0
Last Updated: 27 May 2014
This lesson will illustrate the steps necessary to configure all of the network interfaces of the Endian appliance after the initial configuration.
Endian Network Architecture
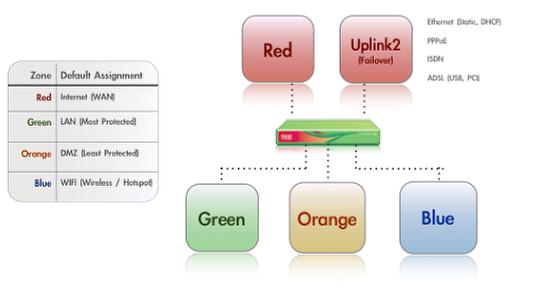
Before we begin the configuration process, please take a moment to familiarize yourself with the color-coded network zones available in the Endian platform and how they are intended to be used (pictured above).
Choose RED (WAN) Interface Type
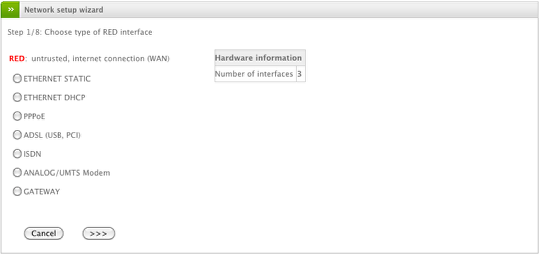
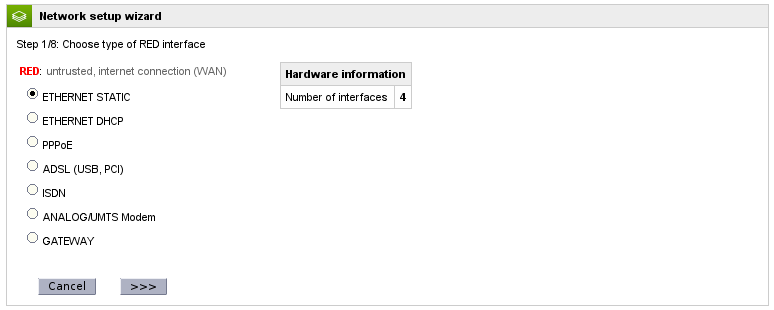
The first step is to choose the connection type of your primary WAN interface. In most cases the proper selection is either Ethernet Static or DHCP unless you require one of the other specific connection types. Click the Forward button 
 to continue.
to continue.
Note
Add Network Zones
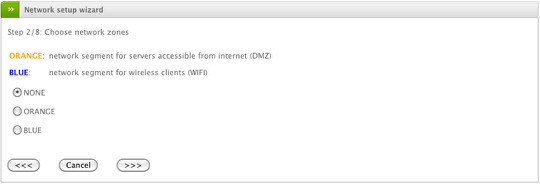

The next option will allow you to select any additional network zone you wish to have configured on your Endian appliance. The available options will depend on the total number of available Ethernet NIC's on the Endian device. Your options could include adding the Blue zone (Wifi) or Orange zone (DMZ) or both. Click the Forward button to continue.
In this example only the blue zone is activated.
Configure Network Zones

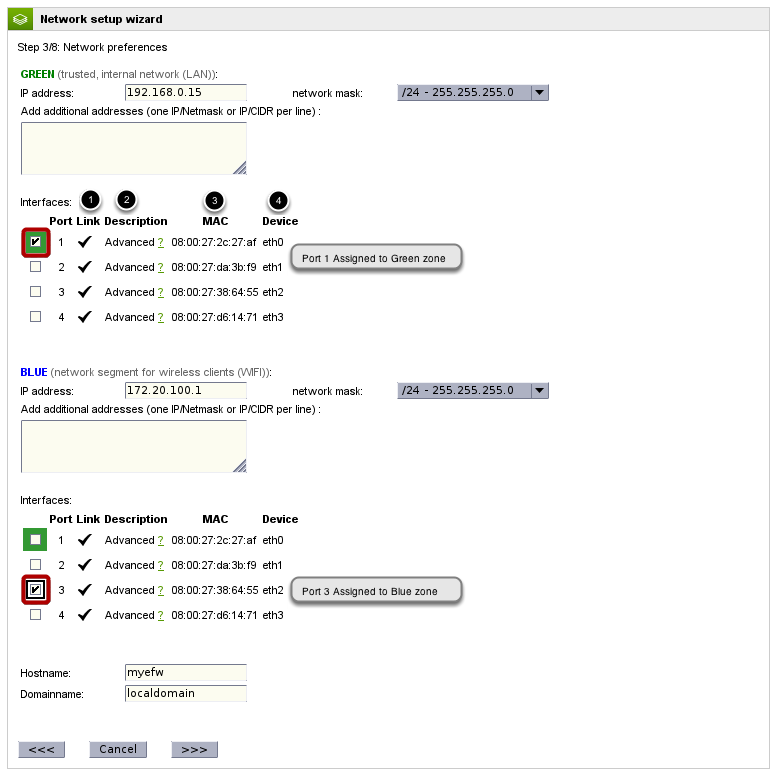
The next step involves configuring the actual IP address you want assigned to the Endian device for each existing network zone. The default Green IP is provided for you but you can use any IP address and subnet you wish. You are also allowed to add additional networks that may co-exist within each single network zone. An example of where this might be used is if you host multiple internal subnets that all need to exist within the same network segment (within one zone).
The blue zone is assigned the network 172.20.100.1/24, hence the Blue interface has IP 172.20.100.1
The next item is a graphical representation of the available physical network interfaces and which zone they are mapped to. You may check or uncheck one or more network interfaces to belong to a network zone (at least one is required) and you may have more than one physical interface per zone; however, you cannot have one physical inteface belong to more than one zone. A network zone with multiple network interfaces will act as a bridge and mimic the behavior of a switch though using an actual physical switch is recommended where performance and efficiency are desired. Next to each network interface port is (1) the link status which indicates if there is a device actually connected to the port, (2) NIC device driver description, (3) network MAC address, and (4) the operating system physical device name.
The last two items are the host and domain name you want assigned to the Endian device itself. Click the Forward button to continue.
Note
- 10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255 (10.0.0.0/8), 16,777,216 addresses
- 172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255 (172.16.0.0/12), 1,048,576 addresses
- 192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255 ( 192.168.0.0/16), 65,536 addresses
Configure Red (WAN) Interface
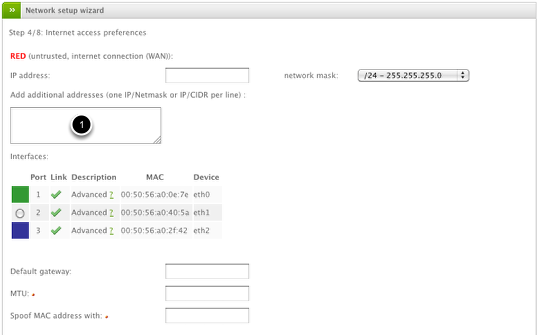
Now you can configure the Red (WAN) interface according to your ISP connection type (as selected during Step 1). The configuration is identical to the previous step where you must configure the IP, subnet, and gateway (if necessary), select the appropriate physical inteface to use for the Red (WAN) connection, and fill out any other ISP connection specific fields.
If you have multiple public IP addresses assigned, you may enter each IP in the "Add additional addresses" field (1). You should list each individual IP in either IP/Netmask or IP/CIDR format with one entry per line (Example: 29.150.10.5/24, 29.150.10.6/24, ...)
The options for MTU is to manually enter a custom value for interface MTU size and is not recommended unless instructed by your ISP. The option to Spoof MAC address with is really only useful for situations where your ISP modem has a "sticky" connection and requires that your Internet MAC address always stay the same. This option would allow you to configure the Endian to "forge" it's Red interface MAC address so you do not lose your ISP connection.
Click the Forward button to continue.
Configure DNS
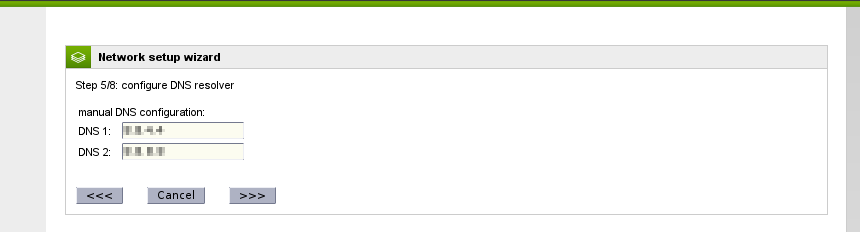
This option is only required if you are not using some form of DHCP for your Red (WAN) connection. You should fill in your ISP-provided or preferred public DNS servers in these fields. Click the Forward button to continue.
Setup Email Information (Optional)
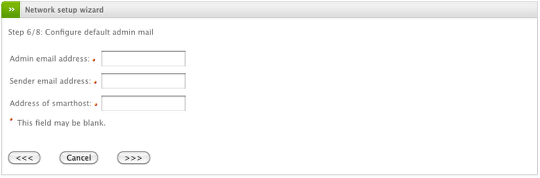
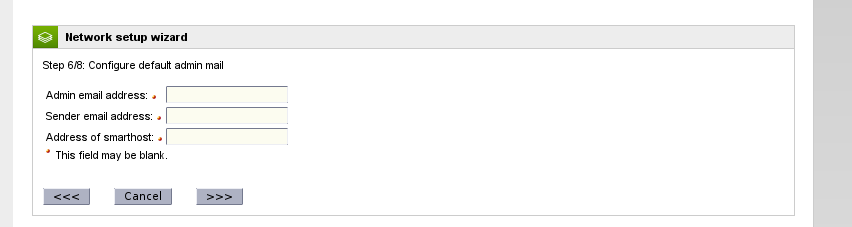
Here you can provide the administrator (recipient) email account along with the Endian (sender) address you want emails from the Endian firewall to use. Also you may specify the address of an email smarthost should you require one. Click the Forward button to continue.
Apply Configuration
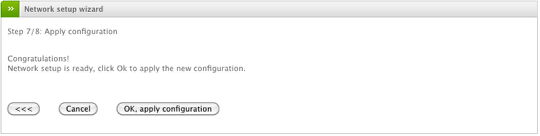
The last step is to apply the configuration to the device. Keep in mind, the changes you made may take up to 20 seconds to be fully applied to the device and for dependent services to be restarted so this may impact any internal device(s) ability to access the device or pass traffic through it. You must access the administration interface of the Endian device using the new IP settings either manually or using the link in the Web UI provided.
Once the network configuration has been successfully completed, you can proceed to register your Endian Appliance to the Endian Network.
My server has two network cards.
I configured a green area with a local network ip. After applying the settings I lose web access.
I realized that creates an interface endian br0 and assign it the ip I set up to the green zone.
I followed the steps correctly. At the server console it shows eth0 without ip. Eth1 with IP network and an external interface (bridge) with the IP that I set up to the green zone.
What I do?
@Paulo I had this same issue. Did you ever get it resolved?
This is the right behaviour, br0 is the GREEN zone and it is used by Endian to create a sort of virtual switches and put into the same broadcast domain more interfaces.
With the command "brctl show" you can see wich interfaces are inside the bridge and belong to a specific zone.